Optimizing Nuclear Plant Outages: Data Analytics Tools and Methods for Enhancing Resilience and Efficiency
Nuclear power plant refueling outages are among the most complex phases in a plant’s operational cycle. During these outages, tens of thousands of activities,
including maintenance and surveillance, are conducted simultaneously within a short timeframe. Typically lasting three to four weeks, these operations involve
large crews of contractors with diverse skill sets performing tasks ranging from testing and surveillance to maintenance. Outages may extend longer if major
backfitting or modernization projects are planned. Consequently, plant outages are expensive incurring significant operational costs such as contractor labor
and equipment, as well as the loss of generation while the plant is offline. This can easily cost a plant operator over a million dollars a day.
Therefore, there is a constant need to mitigate the economic impact on plants by reducing the frequency, duration, and risks associated with these outages.
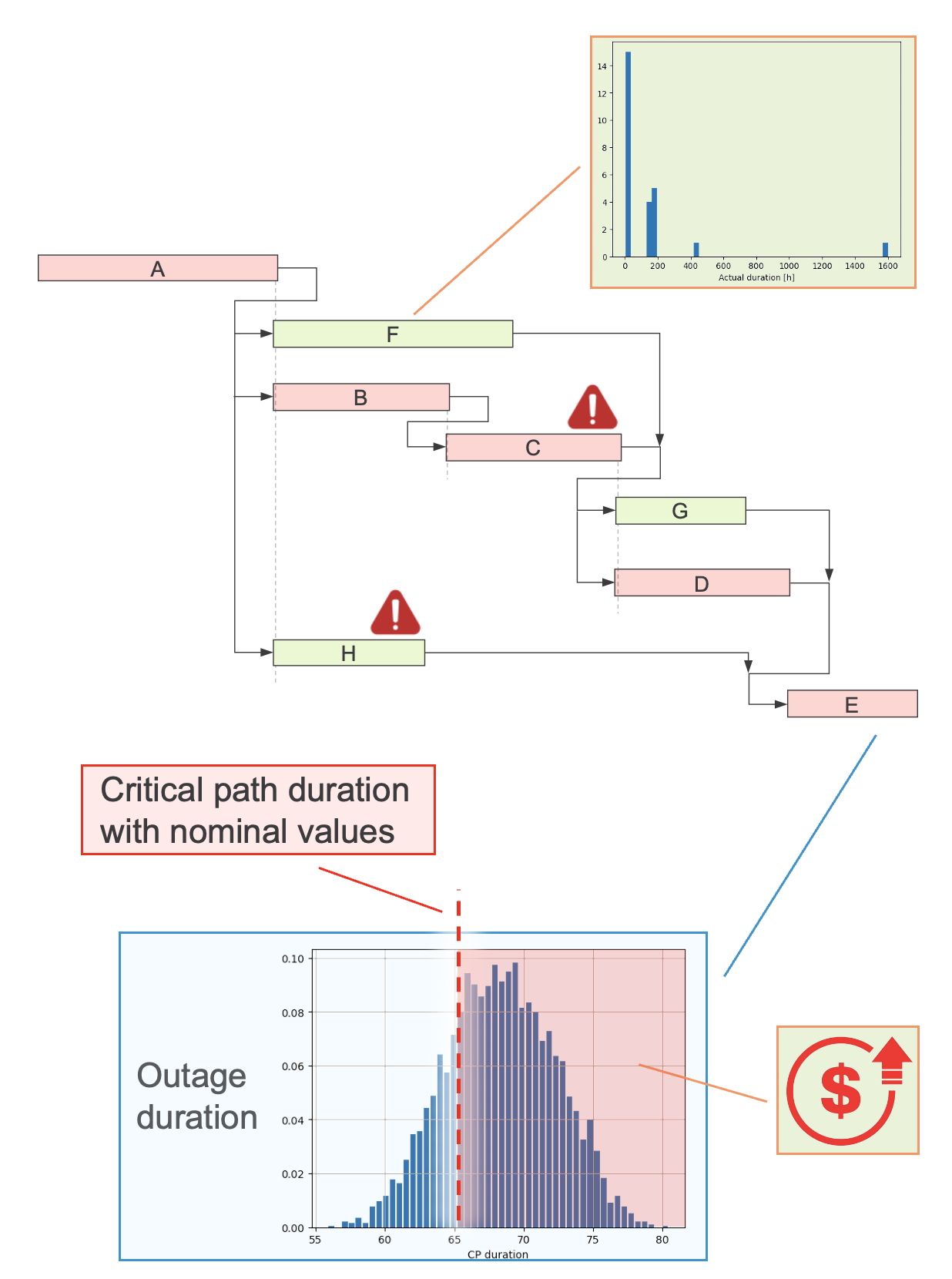
The Outage Optimization project, part of the U.S. Department of Energy’s Light Water Reactor Sustainability Program, is developing openly available tools
and methods to enhance outage scheduling for nuclear power plants. These tools and methods assist outage planners in several critical areas. First, they
assess schedule resiliency by evaluating how the schedule can accommodate delays and adapt to unexpected activities, such as equipment degradation
discovered during planned outage activities. Second, they identify critical points in the outage schedule where potential unplanned issues may arise.
Third, these tools and methods help planners allocate available resources to address delays and unexpected events as the outage progresses, thereby reducing
the risk of delays and ensuring the outage schedule stays on track. By improving outage predictability and resilience, these tools contribute to national
energy security, workforce modernization, and the digital transformation of nuclear operations.
The Outage Optimization project has tackled several use cases, each focusing on different aspects of outage planning and execution. These
use cases are:
ANS Nuclear Newswire article (2025)
Tools and Methods for Optimization of Nuclear Plant Outages
Idaho National Laboratory Technical Report INL/RPT-23-74439 (2023)
Tools And Methods to Analyze Plant Outage Schedules and Assist Schedulers in Improving Outage Resilience
Idaho National Laboratory Technical Report INL-RPT-24-80380 (2024)